Solver
Synopsis
A Solver tries to solve the constraints in a TModel; unsolved constraints produce error messages
Description
The purpose of a Solver is to solve the constraints that have been gathered by the Collector and to produce a TModel. The functions provided by a Solver are summarized below:
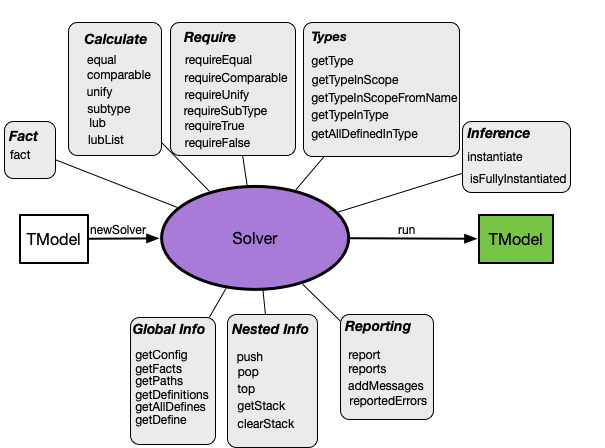
Two dozen functions (some very similar to the ones provided for Collector) are available that fall into the following categories:
- Lifecycle of Solver: create a new Solver and use it to solve the constraints in a given TModel.
- Fact: establish facts.
- Calculate: calculate types.
- Require: check requirements.
- Types: retrieve the type of a program fragment in various ways, if that type is available.
- Inference: create new type variables for type inference.
- Reporting: report errors, warnings and info messages.
- Global Info: access global information such as the current Configuration, available type facts, and the global store (to be explained in more detail below).
In identical style as used for the Collector, Solver is a datatype with a single constructur and with a number of functions as fields, For instance, given a Solver named s, calling the getType function amounts to: s.getType(_argument-of-getType_). All Solver functions are prefixed with /* Solver field */ to emphasize that they are a field of the Solver datatype.
The result of the Solver is an enriched TModel that contains, amongst others, messages regarding violated requirements or types that could not be computed. It can also be used to generate other usefull information about the program such as a use-def relation and the used vocabulary (used for name completion).
Lifecycle of Solver
Once, an initial TModel has been created by a Collector, a Solver takes over to solve constraints and produce a final TModel. A new Solver can be created by newSolver that comes in two flavours:
Solver newSolver(Tree pt, TModel tm)
Solver newSolver(map[str,Tree] namedTrees, TModel tm){
The former takes a parse tree and an initial TModel and is intended to solve the constraints for a single parse tree. The latter takes a map of named parse trees and an initial TModel and can handle the situation of multiple trees with mutual dependencies.
Finally, run creates the final TModel by solving the constraints in the initial TModel:
/* Solver field */ TModel () run
A complete type checking scenario (for a given a parse tree pt of the program to be checked) is:
c = newCollector("my_model", pt); // create Collector
collect(pt, c); // collect constraints
initial_model = c.run(); // create initial TModel
s = newSolver(pt, initial_model); // create Solver
final_model = s.run(); // solve constraints and produce final TModel
The final TModel contains valuable information such as
- messages (errors, warnings, info);
- type facts for subtrees of the given parse tree;
- use/def relations.
Fact
The function fact registers known type information for a program fragment src:
/* Solver field */ void (value src, AType atype) fact
Here
srcmay either be aTree(i.e., a parse tree fragment) or aloc(the source location of a parse tree fragment).atypeis the AType to be associated withsrc.
Calculate
All calculate (and require) functions use the following typing convention: an argument of type value can either be:
- an
AType, or - a
Tree.
In the former case, the AType is used as is. In the latter case, the type of the tree is used provided that it exists. Otherwise a TypeUnavailable() exception is generated and the calculator or requirement in which the predicate occurs is re-evaluated at a later time.
equal
/* Solver field */ bool (value l, value r) equal
The function equal determines whether the types of l and r are equal, the result is a Boolean value.
subtype
/* Solver field */ bool (value l, value r) subtype
The function subtype determines whether the type of l is a subtype of the type of r; it calls the user-provided function getSubType, see Configuration.
comparable
/* Solver field */ bool (value l, value r) comparable
The function comparable determines whether the type of l is comparable with the type of r; it calls the user-provided function getSubType twice, see Configuration.
unify
/* Solver field */ bool (value l, value r) unify
The function unify determines whether the type of l can be unified with the type of r it calls the user-provided functions getSubType and getLub, see Configuration. The bindings that may result from unification are effectuated when the enclosing calculate succeeds.
lub
/* Solver field */ AType (value l, value r) lub
The function lub return the least upper bound of the types of l and r; it calls the user-provided function getLub, see Configuration.
requireEqual
/* Solver field */ void (value l, value r, FailMessage fmsg) requireEqual
The function requireEqual returns when the types of l and r are equal, otherwise a FailMessage is reported.
requireSubType
/* Solver field */ void (value l, value r, FailMessage fmsg) requireSubType
The function requireSubtype returns when the type of l is a subtype of r, otherwise the FailMessage is reported;
it calls the user-provided function getSubType, see Configuration.
requireCompare
/* Solver field */ void (value l, value r, FailMessage fmsg) requireComparable
The function requireComparable returns when the type of l is comparable with the type of r, otherwise the FailMessage is generated; it calls the user-provided function getSubTypetwice, see Configuration.
requireUnify
/* Solver field */ void (value l, value r, FailMessage fmsg) requireUnify
The function requireUnify just returns when the type of lcan be unified with the type ofr, otherwise the FailMessage is reported; it calls the user-provided functions getSubTypeandgetLub`, see Configuration. The bindings that may result from unification are effectuated when the enclosing require succeeds.
requireTrue and requireFalse
/* Solver field */ void (bool b, FailMessage fmsg) requireTrue
/* Solver field */ void (bool b, FailMessage fmsg) requireFalse
The function requireTrue returns when its condition is true, otherwise the FailMessage is reported. The function requireFalse returns when its condition is false, otherwise the FailMessage is reported.
Types
Type-related functions try to retrieve various forms of type information from parts of the source program. When that information is available, it is returned as result. When it is not available, the internal exception TypeUnavailable() is thrown. This will abort the execution of the current requirement or calculator which will then be tried later again.
getType
The workhorse of TypePal is the function getType that determines the type of a given source code fragment in the current scope:
/* Solver field */ AType(value src) getType
src may either be a Tree (i.e., a parse tree fragment) or a loc (the source location of a parse tree fragment).
Here is how getType is used in the Pico example to check the addition operator:
- two integer arguments give an integer result;
- two string arguments give a string result;
- other combinations are incorrect.
void collect(current: (Expression) `<Expression lhs> + <Expression rhs>`, Collector c){
c.calculate("addition", current, [lhs, rhs],
AType (Solver s) { switch([s.getType(lhs), s.getType(rhs)]){
case [intType(), intType()]: return intType();
case [strType(), strType()]: return strType();
default:
s.report(error(current, "Operator `+` cannot be applied to %t and %t", lhs, rhs));
}
});
collect(lhs, rhs, c);
}
getTypeInScope
The function getTypeInScope determines the type of a given source code fragment in a given scope and given roles:
/* Solver field */ AType (Tree occ, loc scope, set[IdRole] idRoles) getTypeInScope
Here
occis a parse tree fragment;scopeis the desired scope;idRolesis a set of allowed identifier roles.
getTypeInScopeFromName
The function getTypeInScopeFromName determines the type of a given name that has been bound via given identifier roles in a given scope. It is typically used to map a name of a type to its actual type, e.g., mapping the name POINT as it occurs in a declaration to the actual record type of POINT.
/* Solver field */ AType (str name, loc scope, set[IdRole] idRoles) getTypeInScopeFromName
Here:
nameis the name of the desired element;scopeis the desired scope;idRolesis a set of allowed identifier roles.
getTypeInType
The function getTypeInType is typically used to determine parts of a container type such as, e.g., the fields in a named record type or the methods in a named class type.
/* Solver field */ AType (AType containerType, Tree selector, set[IdRole] idRolesSel, loc scope) getTypeInType
Here:
containerTypeis a given container type;selectoris a parse tree fragment to select a part from the container type (e.g., a field or method name);idRolesSelis a set of allowed identifier roles for the selector (e.g.,fieldId()ormethodId());scopeis the desired scope.
getAllDefinedInType
The function getAllDefinedInType is typically used to determine all named types that are defined in a container type,
e.g., all fields in a record type or all methods in a class type.
/* Solver field */ rel[str id, AType atype] (AType containerType, loc scope, set[IdRole] idRoles) getAllDefinedInType
Here:
containerTypeis a given container type;scopeis the desired scope;idRolesis a set of allowed identifier roles for the selectoed types.
Inference
Type inference is supported by the introduction of type variables using newTypeVar in combination with unification primitives inside calculateEager Calculate and requireEager Require such as requireUnify and unify. The following functions support the computation with types possibly containing type variables.
instantiate
/* Solver field */ AType (AType atype) instantiate
Replaces all type variables occurring in atype by their binding (when present).
isFullyInstantiated
/* Solver field */ bool (AType atype) isFullyInstantiated
checks whether atype contains any occurrences of type variables.
Reporting
/* Solver field */ bool(FailMessage fmsg) report
/* Solver field */ bool (list[FailMessage] fmsgs) reports
/* Solver field */ bool () reportedErrors
A single message (report), or multiple messages can be reported (reports). The function reportedErrors returns true if any error has been reported.
getConfig
/* Solver field */ TypePalConfig () getConfig
Returns the current Configuration.
getFacts
/* Solver field */ map[loc, AType]() getFacts
Returns the current fact base as mapping from source locations to atypes.
getPaths
/* Solver field */ Paths() getPaths
Returns all the paths known to the Solver.
getDefinitions
/* Solver field */ set[Define] (str id, loc scope, set[IdRole] idRoles) getDefinitions
Returns all the defines for a given identifier.
getAllDefines
/* Solver field */ set[Define] () getAllDefines
Returns all the defines.
getDefine
/* Solver field */ Define(loc) getDefine,
Returns the define associated with a given source location.
getStore
/* Solver field */ map[str,value]() getStore
Returns the global store of the Solver. The global store is a key-value store intended to share information between Collector and Solver as well as pass on information to later users of the typechecker as a whole. Examples taken from the Rascal typechecker include:
- The name of the current module.
- The bill-of-materials (BOM) of the current module, i.e., all used modules including a time stamp.
- The PathConfig used for typechceking.
- The grammar rules defined in the module
- The data declarations defined in the module
It is also possible to create an arbitrary number of (named) of push down stacks in the global store. These can be used to represent context information during the collect or solve phase, see Nested info.
With the availability of a global store come serious responsibilities. Don't overuse it, do not misuse it.